网站:https://github.com/numpy/numpy
文档:https://numpy.org/doc
源代码:https://github.com/numpy/numpy
源码中有很多以C实现的代码,有一定的参考性:
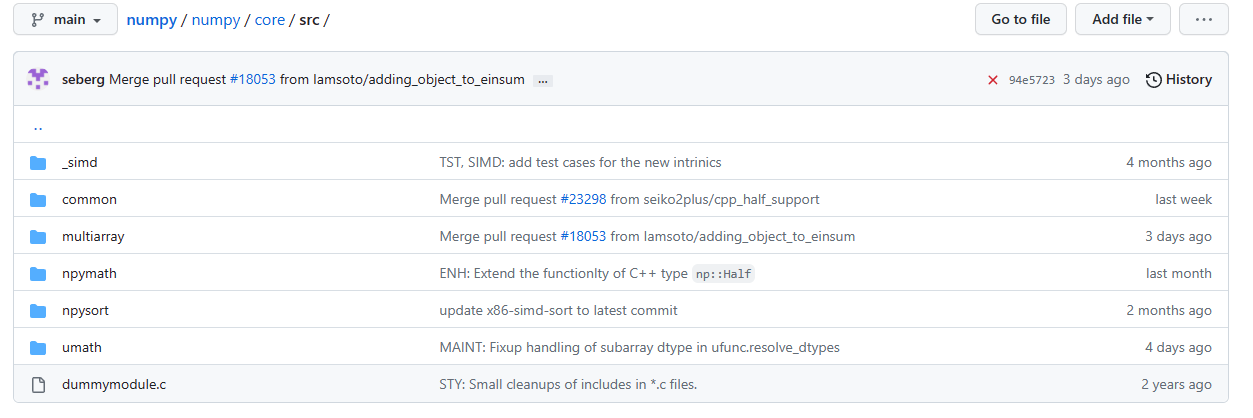
比如单精度浮点转半精度浮点
[C] 纯文本查看 复制代码 uint16_t numpy_floatbits_to_halfbits(uint32_t f) {
uint16_t h_sgn = (uint16_t)((f & 0x80000000u) >> 16);
uint32_t f_exp = f & 0x7f800000u;
uint32_t f_sig = f & 0x007fffffu;
// Exponent overflow/NaN converts to signed inf/NaN
if (f_exp >= 0x47800000u) {
if ((f_exp == 0x7f800000u) && (f_sig != 0)) {
// NaN - propagate the flag in the significand...
uint16_t ret = (uint16_t)(0x7c00u + (f_sig >> 13));
ret += (ret == 0x7c00u); // ...but make sure it stays a NaN
return h_sgn + ret;
} else {
// (overflow to) signed inf
return (uint16_t)(h_sgn + 0x7c00u);
}
}
// Exponent underflow converts to a subnormal half or signed zero
if (f_exp <= 0x38000000u) {
// Signed zeros, subnormal floats, and floats with small
// exponents all convert to signed zero half-floats.
if (f_exp < 0x33000000u) {
return h_sgn;
}
// Make the subnormal significand
f_exp >>= 23;
f_sig += 0x00800000u;
f_sig >>= (113 - f_exp);
// Handle rounding by adding 1 to the bit beyond half precision
//
// If the last bit in the half significand is 0 (already even),
// and the remaining bit pattern is 1000...0, then we do not add
// one to the bit after the half significand. However, the
// (113 - f_exp) shift can lose up to 11 bits, so the || checks
// them in the original. In all other cases, we can just add one.
if (((f_sig & 0x3fffu) != 0x1000u) || (f & 0x07ffu)) {
f_sig += 0x1000u;
}
uint16_t h_sig = (uint16_t)(f_sig >> 13);
// If the rounding causes a bit to spill into h_exp, it will
// increment h_exp from zero to one and h_sig will be zero.
// This is the correct result.
return (uint16_t)(h_sgn + h_sig);
}
// Regular case with no overflow or underflow
uint16_t h_exp = (uint16_t)((f_exp - 0x38000000u) >> 13);
// Handle rounding by adding 1 to the bit beyond half precision
//
// If the last bit in the half significand is 0 (already even), and
// the remaining bit pattern is 1000...0, then we do not add one to
// the bit after the half significand. In all other cases, we do.
if ((f_sig & 0x3fffu) != 0x1000u) {
f_sig += 0x1000u;
}
uint16_t h_sig = (uint16_t)(f_sig >> 13);
// If the rounding causes a bit to spill into h_exp, it will
// increment h_exp by one and h_sig will be zero. This is the
// correct result. h_exp may increment to 15, at greatest, in
// which case the result overflows to a signed inf.
return (uint16_t)(h_sgn + h_exp + h_sig);
}
| 






 发表于 2023-5-2 04:42:09
发表于 2023-5-2 04:42:09

 发表于 2023-5-9 12:27:22
发表于 2023-5-9 12:27:22
