|
|
LUA脚本的好处是用户可以根据自己注册的一批API(当前TOOL已经提供了几百个函数供大家使用),实现各种小程序,不再限制Flash里面已经下载的程序,就跟手机安装APP差不多,所以在H7-TOOL里面被广泛使用,支持在线调试运行,支持离线运行。
TOOL的LUA教程争取做到大家可以无痛调用各种功能函数,不需要学习成本。

掌握这些基础就够用了。
一、注释
注释、多行注释、取消多行注释:
注释单行
注释多行
取消注释多行
二、变量:
变量
1.变量无需声明
2.变量没声明为nil,赋值为nil等同于删除
3.lua把nil,false视为假,其他都为true
4.Lua中的变量全是全局变量,除非用 local 显式声明为局部变量
5.#ta字符串的长度,也可以获取表格数字索引对应的个数
例子- --全局赋值
- x = 1
- --局部多个赋值
- local x,y = 1,2
- local ta = {1,2,3,name='安富莱'}
- --3
- print(#ta)

三、条件:
条件
if
and or not
>= <= == > < ~=
例子
- if (a >= 0) then --大于等于
- b = b + 1
- else
- b = b - 1
- end
- if (a ~= 0) then --不等于
- end
- if (a==b and c == 0) then --逻辑与
- elseif (a~=b) then --不等于
- elseif (not a) then --逻辑非
- else
- end
四、循环
例子
- local a=10
- while (a < 20)
- do
- a = a + 1
- print(a)
- end
- local t = {1,2,3}
- for i,v in pairs(t) do
- print(v)
- end
--每次加1
- for i=0,5,1 do
- print(i)
- end
--每次减1
- --5,4,3,2,1
- for i=5,1,-1 do
- print(i)
- end

五、函数
例子:
- --声明函数,传递2个参数,返回2个值得和
- function add(num1, num2)
- return num1 + num2
- end
--把函数赋值给一个变量,然后可以当参数传递
- local myprint = function(str)
- print(str)
- end
- function say(arg1,func)
- func(arg1)
- end
- --www.freecls.com
- say('www.freecls.com',myprint)
--可变参数
- function average(...)
- result = 0
- local arg={...}
- for i,v in ipairs(arg) do
- result = result + v
- end
- print("总共传入 " .. #arg .. " 个数")
- return result/#arg
- end
- function what()
- return '安富莱','www.armlfy.com'
- end
- --返回多个参数
- local name,url = what()
- print(name,url)

五、常用字符串函数:
string.byte(s [, i [, j]])
string.byte是用来把字符转换成ascii数字,
s为目标字符串,i为索引开始位置(从1开始),j为索引结束位置
例子
- --默认为第1个返回a的ascii值
- local r = string.byte('abcdefg') --97
- --从索引2(b)到索引4(d)也就是分别返回bcd的ascii值
- local r1,r2,r3 = string.byte('abcdefg',2,4) --98,99,100
string.char(...)
string.char是把ascii数值转换成字符
例子
- --返回98所对应的字符
- local r = string.char(98) --a
- --返回98,,99,100对应的字符并连在一起返回
- local r = string.char(98,99,100) --abc
string.sub (s, i [, j])
截取字符串(字符串分割,字符串截取),i为起始索引,可选参数j为结束索引(包含),都可以为负数,第一个字符索引为1,最后一个字符为-1
例子
- local res,s
- s = 'www.armfly.com'
- res = string.sub(s,5) --armfly.com
- res = string.sub(s,5,-1) --armfly.com
- --截取后3位
- res = string.sub(s,-3) --com
- --截取前3位
- res = string.sub(s,1,3) --www
string.find (s, pattern [, init [, plain]])
字符串查找函数找不到返回nil,找到了返回开始位置和结束位置,
init为从哪里开始默认为1,plain默认为false表示利用模式匹配,
如果设为true则表示纯文本匹配(也就是关闭正则匹配)
例子
- local str = 'i love programming,11,22,%d+aa'
- local s = string.find(str,'222') --nil
- s = string.find(str,'pro') --8
- s = string.find(str,",%d+") --19(匹配到了,11)
- s = string.find(str,",%d+",1,true) --25(由于关闭了模式匹配,所以匹配到了,%d+)
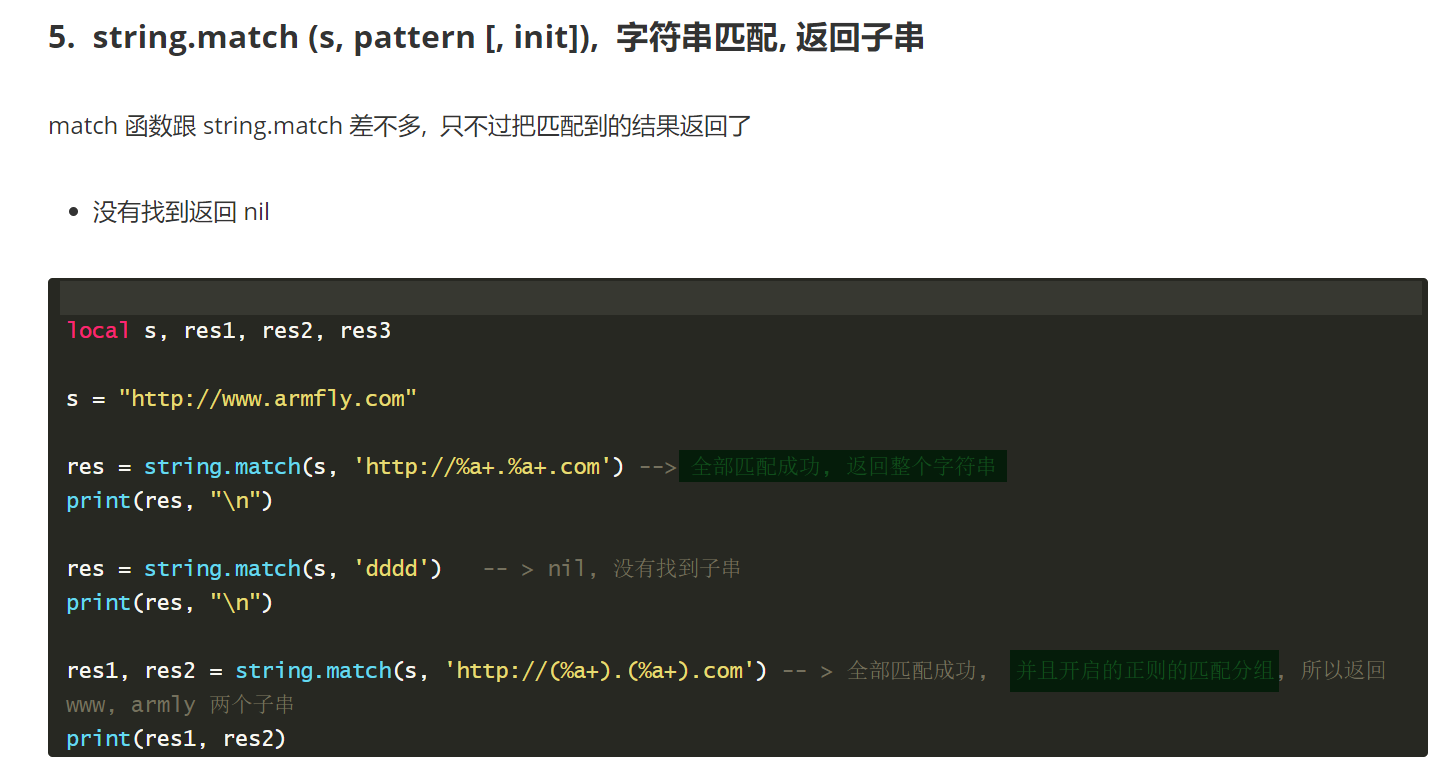
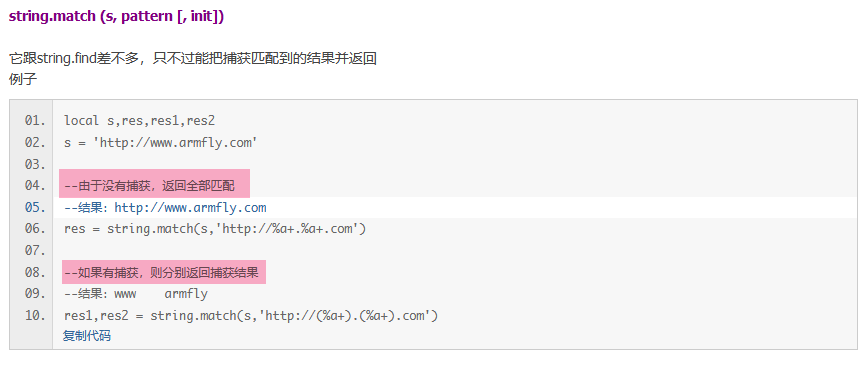
string.match (s, pattern [, init])
它跟string.find差不多,只不过能把捕获匹配到的结果并返回
例子
- local s,res,res1,res2
- s = 'http://www.armfly.com'
- --由于没有捕获,返回全部匹配
- --结果:http://www.armfly.com
- res = string.match(s,'http://%a+.%a+.com')
- --如果有捕获,则分别返回捕获结果
- --结果:www armfly
- res1,res2 = string.match(s,'http://(%a+).(%a+).com')
string.gsub (s, pattern, repl [, n])
用来做字符串替换,可选参数n代表替换多少次默认全部替换,
返回替换后的字符串,也可以指定第二个返回值为替换的次数。
例子
- local s,res,res1,res2
- s = 'http://www.armfly.com'
- --结果:http://test.armfly.com,1
- res,count = string.gsub(s,'www','test')
- --捕获替换
- --结果:test.freecls.abc
- res = string.gsub(s,'^http://%w+.(%w+).com$','test.%1.abc')
- --w替换成t,但是只替换2次
- --结果:http://ttw.armfly.com
- res = string.gsub(s,'w','t',2)
string.format (formatstring, ···)
字符串格式化类型c语言的sprintf不说废话以例子来讲解
- local s = string.format('%d%s',123,'armfly') --123armlfy
- s = string.format('%0.2f',1.234343) --1.23(保留2位)
- --转成16进制,%X为大写的16进制
- local s = string.format('%X',140) --8C
- local s = string.format('%x',140) --8c
- local s = string.format('%04x',140) --008c
string.len(s)
返回字符串长度=#s
string.rep(s,n)
字符串重复n次并拼接返回
string.lower(s)
转小写
string.upper(s)
转大写
string.reverse(s)
反转字符串
|
|







 发表于 2021-12-4 00:07:04
发表于 2021-12-4 00:07:04




 楼主
楼主 发表于 2021-12-6 11:15:52
发表于 2021-12-6 11:15:52
 系统学习下 Lua
系统学习下 Lua
 期待
期待